Local And Convective Acceleration
Local And Convective Acceleration. The last three terms make up the convective acceleration, which is defined as the acceleration due to convection or movement of the fluid particle to a different part of the flow field. The first term of the expression for the acceleration is the local acceleration, which is nonzero for unsteady flow.
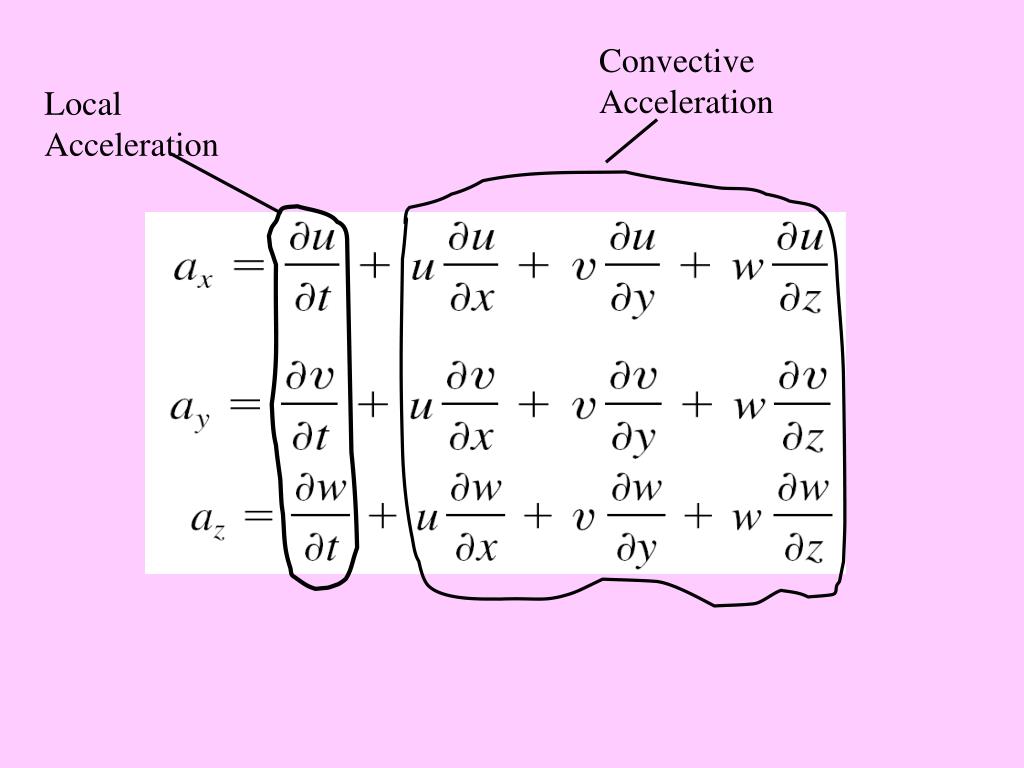
The first term on the right hand side is called the local acceleration or the unsteady acceleration. This video explains about local and convective acceleration. Local acceleration = ∂u/∂t i + ∂v/∂t j + ∂w/∂t k = 0 i + 0 j + 0 k (result) convective acceleration vector = u ∂ v /∂x + v ∂ v /∂y + w ∂ v /∂z = 4x i + 4y j + z k ft/sec 2 (result)
To Investigate The Relative Effects Of The Local And Convective Terms, We Define A Reference For The Local Acceleration, A L ¼ 1 Þ 1=2 3 1 G Qf Y Qt Y¼0 ¼ Eky Þoð 3Þ (15) And A Reference For The Nonlinear Convective Term A C ¼ 1 2 Þ 1=2 4.
V⋅∇v is the convective part. The local accn changes because the flow is not steady and time dependent, and the values are as you have derived. This video explains about local and convective acceleration.
The Local And Convective Accelerations Of Steep Irregular Wave Events Have Been Investigated.
(i) local acceleration which is a velocity change with respect to time at a given point, occurring when the flow is unsteady, and (ii) convective acceleration which is associated with spatial gradients of velocity in the flow field. The rate of increase of velocity with respect to time at a given point in a given fluid flow is called the local acceleration. And also explained the problem solving steps on velocity and acceleration of fluid particle in a.
The First Term Of The Expression For The Acceleration Is The Local Acceleration, Which Is Nonzero For Unsteady Flow.
Local acceleration or temporal acceleration is defined as the rate of change of velocity with respect to time at a given point in a flow field. The acceleration of an element of fluid, given by the convective derivative of the velocity , where is the gradient operator. Let us consider that ax, ay and az are the total acceleration in x, y and z direction respectively.
Finds And Reports Local Value Of G, The Acceleration Of Gravity At A Location (City,State In Us) Send Feedback | Visit Wolfram|Alpha.
Given the velocity field is described in eulerian terms as, v = xyt i + 6z j + xz2 k find the local acceleration, convective acceleration, and total acceleration of a particle in terms of x, y, z, and t. In uniform flow, the fluid properties do not vary from point to point at any instant of time, that is, therewill be no spatial variation of fluid properties. Local acceleration = ∂u/∂t i + ∂v/∂t j + ∂w/∂t k = 0 i + 0 j + 0 k (result) convective acceleration vector = u ∂ v /∂x + v ∂ v /∂y + w ∂ v /∂z = 4x i + 4y j + z k ft/sec 2 (result)
Local Acceleration Or Temporal Acceleration Is Defined As The Rate Of Change Of Velocity With Respect To Time At A Given Point In A Flow Field.
The first term on the right hand side is called the local acceleration or the unsteady acceleration. The convective acceleration is due to the flow velocity changing from place to place. Considering the chain rule of differentiation, we will have the following equation of.
Post a Comment for "Local And Convective Acceleration"